Introduction:
Hydrocephalus is a complex neurological disorder with the abnormal build-up of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain that results in raised intracranial pressure. It can result in extreme brain damage and even death if not treated promptly. The condition demands early treatment, most commonly a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt surgery. At Greater Noida, Anand Spectrum Hospital has treated many cases of hydrocephalus with success, providing the latest facility of treatment to the patients. This case report gives an account of a case study in which a patient with gross hydrocephalus was successfully treated and recovered.
Case Presentation:
One patient was admitted in Anand Spectrum Hospital in Greater Noida with the history of chronic vomiting and severe headache, which are common presentations for raised intracranial pressure. The patient’s condition had been deteriorating over the last few days, and preliminary clinical assessment pointed towards neurological etiology.
A computed tomography (CT) scan was conducted and showed gross hydrocephalus, a condition where there is a build-up of excess CSF within the ventricles of the brain. The build-up puts pressure within the skull, leading to neurological signs such as the patient’s headache and vomiting.
Surgical Intervention:
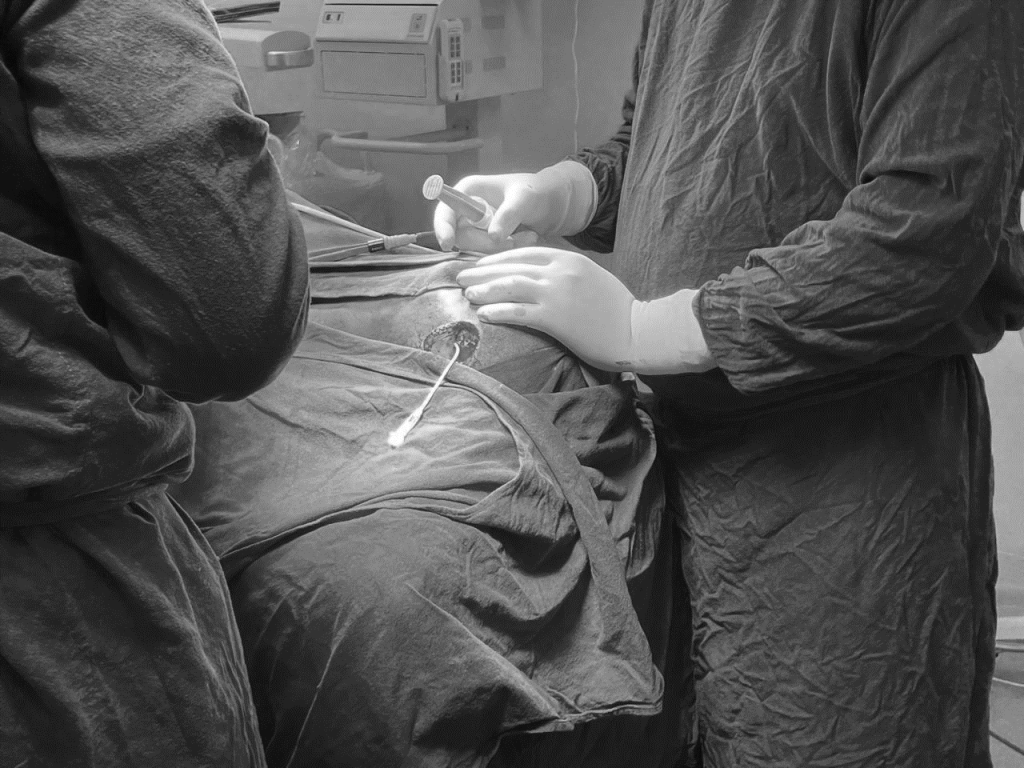
Due to the seriousness of the condition, a decision was made to undergo a VP shunt procedure in full anesthesia immediately. The VP shunt is a surgical intervention where a catheter is inserted into the ventricles to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid into the peritoneal space to alleviate intracranial pressure.
The operation was done without any complication. The adjustment of the shunt placement was done with care to allow proper fluid drainage and maintain the patient’s vital signs stable throughout the operation. The intervention was critical in preventing further damage to the nerves and stabilizing the patient.
Post-Operative Care:
The patient’s post-operative recovery at Anand Spectrum Hospital was diligently kept under check. The patient was remarkably better within 24 hours of surgery. Vomiting and headaches had ceased, and neurological function had returned to normal levels. Imaging following surgery established successful placement of the shunt with notable reduction of fluid accumulation in the brain.
Discharge and Follow-Up:
Following observation for a few days, the patient was discharged in stable condition with proper follow-up instructions. The patient was instructed to come for follow-up check-ups at regular intervals to ensure the proper functioning of the VP shunt and to check for signs of complications.
Conclusion:
This case is an example of the need for early diagnosis and prompt surgical intervention in the management of gross hydrocephalus. At Greater Noida’s Anand Spectrum Hospital, cutting-edge neurosurgical treatment, including VP shunt surgeries, is saving lives and enabling patients with neurological disorders to lead a good quality of life again. This success story highlights the hospital as an authority in providing critical care to patients with hydrocephalus in the Greater Noida area.
By combining cutting-edge technology, talented neurosurgeons, and extensive post-operative care, Anand Spectrum Hospital continues to provide state-of-the-art solutions for complex neurological disorders.